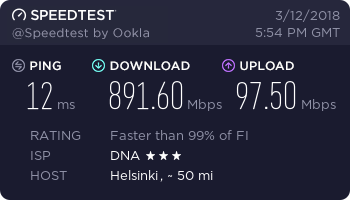
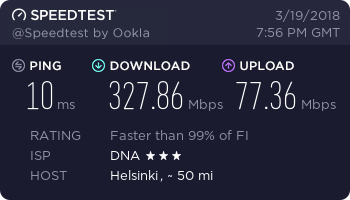
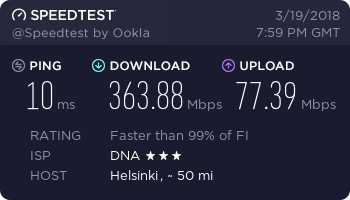
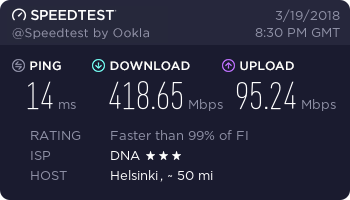
Hardware: Lenovo ThinkPad W550s with Sierra Wireless EM7345
Software: Debian 10 (buster/testing)
Operator: Sonera (Finland)
After Debian installation the modem is recognized, but somehow a working connection just can’t be created:
# mmcli -L
Found 1 modems:
/org/freedesktop/ModemManager1/Modem/0 [Sierra Wireless Inc.] Sierra Wireless EM7345 4G LTE
# mmcli -m 0
/org/freedesktop/ModemManager1/Modem/0 (device id '<snip>')
-------------------------
Hardware | manufacturer: 'Sierra Wireless Inc.'
| model: 'Sierra Wireless EM7345 4G LTE'
| revision: 'V1.1,11'
| H/W revision: 'unknown'
| supported: 'gsm-umts, lte'
| current: 'gsm-umts, lte'
| equipment id: '<snip>'
-------------------------
System | device: '/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:14.0/usb2/2-4'
| drivers: 'cdc_acm, cdc_ncm'
| plugin: 'Generic'
| primary port: 'ttyACM0'
| ports: 'enx000011121314 (net), ttyACM0 (at), ttyACM2 (at)'
-------------------------
Numbers | own : 'unknown'
-------------------------
Status | lock: 'none'
| unlock retries: 'sim-pin (3), sim-pin2 (3), sim-puk (10), sim-puk2 (10)'
| state: 'registered'
| power state: 'on'
| access tech: 'lte'
| signal quality: '35' (recent)
-------------------------
Modes | supported: 'allowed: 2g, 3g, 4g; preferred: none'
| current: 'allowed: 2g, 3g, 4g; preferred: none'
-------------------------
Bands | supported: 'unknown'
| current: 'unknown'
-------------------------
IP | supported: 'ipv4, ipv6, ipv4v6'
-------------------------
3GPP | imei: '<snip>'
| enabled locks: 'none'
| operator id: '24491'
| operator name: 'FI SONERA'
| subscription: 'unknown'
| registration: 'home'
| EPS UE mode: 'csps-2'
-------------------------
SIM | path: '/org/freedesktop/ModemManager1/SIM/0'
-------------------------
Bearers | paths: '/org/freedesktop/ModemManager1/Bearer/0'
# nmcli connection add type gsm ifname "" con-name 4G apn internet connection.autoconnect no
Connection '4G' (ef2b6f2d-e072-44cf-a9f8-831b79b179f2) successfully added.
# nmcli connection up 4G
Error: Connection activation failed: Unknown error
daemon.log revealed that modem got stuck on “Connect: ppp0 <–> /dev/ttyACM0” and a bit later on “Couldn’t initialize PDP context with our APN: ‘Serial command timed out'”
Problem seems to be that NCM -mode isn’t actually supported by EM7345 – even though advertised by the firmware (and H/W revision says unknown). Small confirmation for this theory is that Lenovo provides drivers for older Windows versions where MBIM isn’t natively supported.
Let’s override defaults for cdc_ncm and prefer MBIM -mode.
# cat /sys/module/cdc_ncm/parameters/prefer_mbim
N
# echo "options cdc_ncm prefer_mbim=Y" > /etc/modprobe.d/cdc_ncm.conf
# modprobe -r cdc_mbim cdc_ncm
# modprobe cdc_mbim
# cat /sys/module/cdc_ncm/parameters/prefer_mbim
Y
# systemctl restart ModemManager
# mmcli -L
Found 1 modems:
/org/freedesktop/ModemManager1/Modem/0 [Sierra Wireless Inc.] MBIM [1199:A001]
# mmcli -m 0
/org/freedesktop/ModemManager1/Modem/0 (device id '<snip>')
-------------------------
Hardware | manufacturer: 'Sierra Wireless Inc.'
| model: 'MBIM [1199:A001]'
| revision: 'FIH7160_V1.2_WW_01.1616.01'
| H/W revision: 'XMM7160_V1.2_MBIM_GNSS_NAND_RE'
| supported: 'gsm-umts, lte'
| current: 'gsm-umts, lte'
| equipment id: '<snip>'
-------------------------
System | device: '/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:14.0/usb2/2-4'
| drivers: 'cdc_acm, cdc_mbim'
| plugin: 'Sierra'
| primary port: 'cdc-wdm0'
| ports: 'wwp0s20u4 (net), cdc-wdm0 (mbim), ttyACM0 (at), ttyACM2 (at)'
-------------------------
Numbers | own : 'unknown'
-------------------------
Status | lock: 'none'
| unlock retries: 'sim-pin2 (3)'
| state: 'registered'
| power state: 'on'
| access tech: 'lte'
| signal quality: '35' (recent)
-------------------------
Modes | supported: 'allowed: 2g, 3g, 4g; preferred: none'
| current: 'allowed: 2g, 3g, 4g; preferred: none'
-------------------------
Bands | supported: 'unknown'
| current: 'unknown'
-------------------------
IP | supported: 'ipv4, ipv6, ipv4v6'
-------------------------
3GPP | imei: '<snip>'
| enabled locks: 'fixed-dialing'
| operator id: '24491'
| operator name: 'FI SONERA'
| subscription: 'unknown'
| registration: 'home'
| EPS UE mode: 'csps-2'
-------------------------
SIM | path: '/org/freedesktop/ModemManager1/SIM/0'
-------------------------
Bearers | paths: 'none'
# nmcli connection up 4G
Error: Timeout expired (90 seconds)
…but still not quite there.
This time daemon.log says that the modem was stuck in 3GPP Registration state loop, idle -> registering -> home -> idle.
Reason for this behavior is Sonera, which (still) doesn’t support IPv6, and somehow fails the handshake if IP type ipv4v6 is offered first. Debug was done by running simple-connect manually:
# systemctl restart ModemManager
# mmcli -m 0 --simple-connect="apn=internet,ip-type=ipv4"
successfully connected the modem
# mmcli -m 0 --simple-disconnect
successfully disconnected all bearers in the modem
# systemctl restart ModemManager
# mmcli -m 0 --simple-connect="apn=internet,ip-type=ipv4v6"
error: couldn't connect the modem: 'Timeout was reached'
# systemctl restart ModemManager
# mmcli -m 0 --simple-connect="apn=internet,ip-type=ipv4"
successfully connected the modem
# mmcli -m 0 --simple-disconnect
successfully disconnected all bearers in the modem
So, how to translate this to network-manager actually handling the connection? Luckily just ignoring IPv6 altogether changes ip-type -setting, so (with nmcli) this is quite easily fixable:
# nmcli connection modify 4G ipv6.method ignore
# nmcli connection up 4G
Connection successfully activated (D-Bus active path: /<snip>)
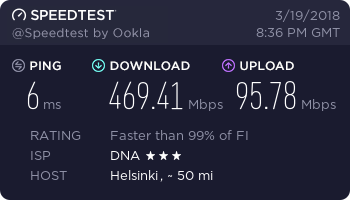
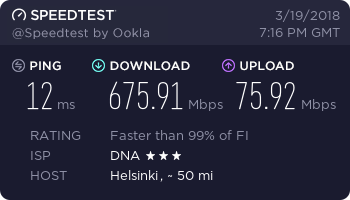
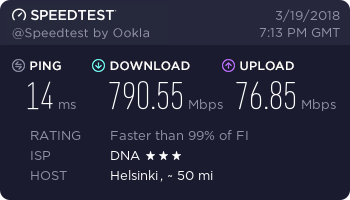
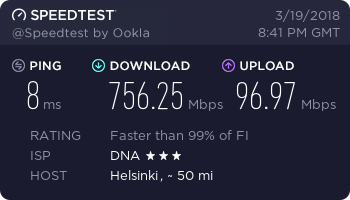
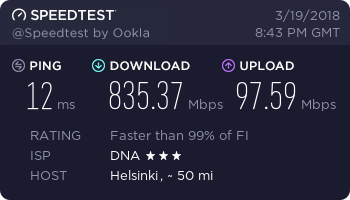
…and finally, a working connection.